What Are The Stabilizer Muscles?
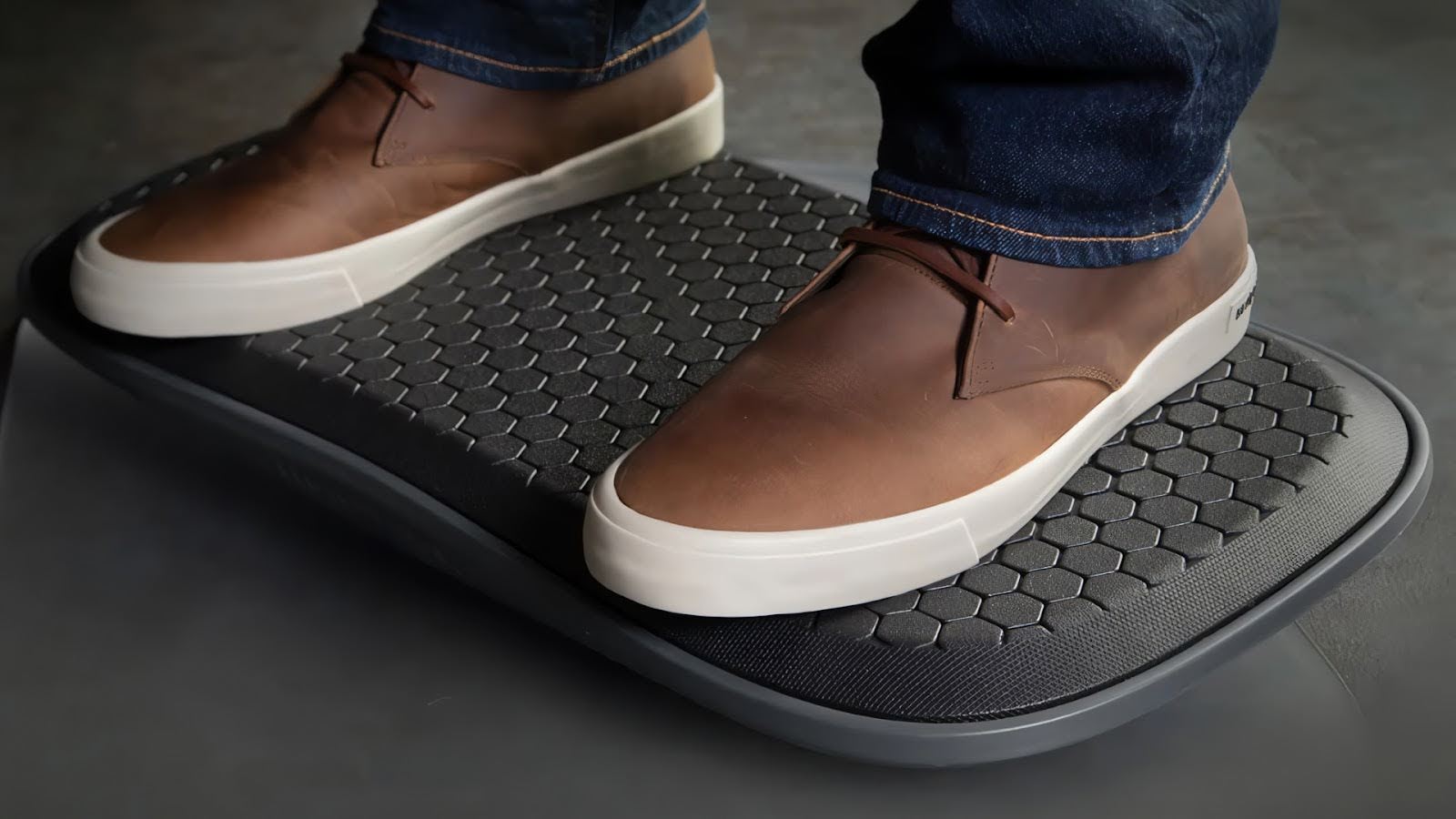

Definition: Stabilizer muscles stabilize the body and its extremities during multi-planar movement.
Science: The primary movers are the muscles doing the majority of the work — they move the load and are often where you really feel the exercise. While the stabilizer muscles aren’t directly involved with moving the load, they work to keep certain parts of the body stable and steady so the primary movers can do their jobs efficiently.
Examples:
- Take The Bench Press For Example. Your rear delts are the main stabilizer muscles during this exercise. They help you control and decelerate the bar or dumbbells effectively. When the bar reaches parallel and goes behind your body, this is a very important role, as you want to prevent injury and stabilize the weight so the primary movers (pectoralis major and the triceps brachii) can press the weight back up.
- Consider The Pull Up: Your triceps act as the main stabilizer during this exercise, while your latissimus dorsi and teres major are the primary movers.
Key Takeaways:
- Maintain Balance And Posture: Stabilizer muscles play a crucial role in maintaining balance and posture, supporting joint and spinal alignment during physical activities, especially in dynamic work environments.
- Constant Engagement: Engaging and strengthening stabilizer muscles through movement-rich environments can prevent injuries, enhance physical health, and foster better mental focus and productivity.
- Studies Show 83% Of FluidStance Users feel happier and 76% more comfortable. Users also experienced stronger stabilizer muscles.
Why Are Stabilizer Muscles Important?
Life has a way of pushing and pulling us emotionally and physically throughout our day. Our stabilizer muscles work to maintain our Center of Mass to allow our core muscles to make big strides. The same is true at your desk. Stabilizer muscles play a crucial role in our physical activities and enable joy and productivity in our work lives. Found throughout the body, they act as the body’s natural support system, enabling us to maintain balance and posture, particularly during movement.
Whether you're using a standing desk, taking a brief walk, or engaging in a quick stretch during your workday, your stabilizer muscles are at the core of these activities, ensuring you perform them safely and effectively.

The Role Of Stabilizer Muscles In Movement
Stabilizer muscles are not the primary movers that execute significant actions like lifting or running; instead, they work quietly in the background, providing the necessary support for our joints and spine, ensuring that we can perform tasks both big and small with precision and safety.
Imagine your body as a sophisticated structure, where every movement, no matter how minimal, is supported by an intricate network of muscles. The stabilizer muscles act as the scaffolding for this structure, offering the stability needed for our primary muscles to function effectively. This enhances your capacity for movement while significantly reducing the risk of injury.
In workplace contexts, especially when incorporating standing desks into routines, it’s crucial to understand and engage these muscles. Active movement awakens our primary muscles and enlivens the unsung heroes of our muscular system.
How Stabilizer Muscles Differ From Prime Movers
Prime movers, or agonist muscles, are the primary muscles responsible for executing specific movements. When we think about exercising, these muscles generally come to mind – the biceps during a curl and the quads during a squat. They're the stars of the show, contracting forcefully to create movement.
Stabilizer muscles play a more supportive role. They stabilize one joint so the desired movement can be performed in another. These muscles often work without us even realizing it, engaging subtly to maintain our posture, balance, and movement precision.
Their contribution is less about the grand gesture and more about the finesse and refinement of motion. While prime movers are about power, stabilizers are about poise.
Identifying The Major Stabilizer Muscles In The Human Body
Stabilizer muscles are often ignored in our pursuit of health and vitality, but they play a critical role in athletic and day-to-day activities, especially in the workspace. Understanding which muscles act as stabilizers can be the first step in transforming our work environment into one that promotes an active, healthy lifestyle.
- The Feet Stabilizer Muscles: FluidStance products initiate engagement of the feet’s stabilizer muscles, including the tibialis anterior and peroneals, which support balance and control. Users report first feeling the benefits in these muscles as they adjust to the product's subtle movement. This helps develop strength, agility, and endurance in the feet – essential for long-term posture improvement and injury prevention, making it a critical part of the overall health impact from daily use of FluidStance balance boards.
- The Core Group of stabilizer muscles includes the transversus abdominis, multifidus, diaphragm, and pelvic floor muscles. These muscles work in concert to provide a solid foundation, aid in balance, and prevent injuries. They're crucial for maintaining posture, especially for those embracing the dynamic standing work culture.
- In The Upper Body, the rotator cuff muscles in the shoulder orchestrate a range of motions while ensuring the arm bone stays firmly within its socket. The serratus anterior, which wraps around the rib cage, is instrumental in all movements involving the shoulders and arms, making it vital for anyone who uses a computer or stands at a desk.
- The Lower Body boasts an impressive array of stabilizer muscles as well, with the gluteus medius and minimus standing out for their role in hip stabilization and leg movement.
- The Quadratus Lumborum and the muscles of the lower leg and foot, such as the tibialis anterior, personals, and soleus, are equally vital. These support our weight during standing and walking and help us make slight postural adjustments when using standing desks or engaging in active movement throughout the workday.
The Importance Of Stabilizer Muscles In Athletic Performance
Far from the spotlight claimed by larger, more prominent muscle groups, these stabilizers work tirelessly in the background, ensuring our movements are smooth, efficient, and, most importantly, safe.
Shock Absorbers
Stabilizer muscles act as the body's natural shock absorbers and support system, enabling elite athletes and everyday individuals to perform tasks with grace and efficiency. Whether you're aiming to improve your personal best in a local marathon, hoping to enhance your endurance in cycling, or simply wishing to carry out daily activities with more ease, the role of stabilizer muscles cannot be overstated.
Balance And Posture
Stabilizer muscles contribute to your overall balance and postural alignment, which is crucial in achieving peak athletic performance. The backup is the poise of a ballet dancer, the explosive power of a soccer player making a sudden turn, and the endurance of a marathon runner. Each movement is supported by a symphony of stabilizer muscles, working harmoniously to prevent injury and enhance the body's resilience.

Athletic Performance
Incorporating exercises that focus on strengthening these stabilizer muscles into your routine can significantly improve athletic performance. Exercises such as plank variations and yoga should challenge your balance and require body alignment. Both are excellent ways to engage and strengthen these crucial muscles. Doing so improves your athletic capabilities and contributes to a lifestyle that values active movement and sustainability.
Stabilizer Muscles And Injury Prevention
Stabilizer muscles are nestled deep within your anatomy and are pivotal in maintaining balance and joint alignment, enhancing movement like sitting, standing, walking, and running.
They function as the body's natural bracing system. When appropriately engaged, they distribute the stress of movement evenly, preventing undue strain on any single part of the body.
The act of standing requires a subtle yet constant engagement of stabilizer muscles in the legs, hips, core, and back. This ongoing engagement is pivotal for maintaining posture and protecting the spine and joints from the repetitive stress injuries plaguing the modern professional.
We are athletes at our desks, where daily performance matters just as much as in any physical endeavor. The tools and equipment we use for our jobs affect our ability to excel and remain injury-free. FluidStance products deliver the perfect balance of athleticism and productivity, allowing for constant engagement of key stabilizer muscles, which enhances posture, reduces strain, and supports long-term health.
Final Thoughts
Choosing accessories to promote an active lifestyle like FluidStance’s may help you harness the latent power of your stabilizer muscles, transforming static office hours into an opportunity for movement and growth.
FluidStance embodies this quiet quest for vitality, blending the essence of physical wellness with a profound commitment to environmental sustainability. Let’s make our workspaces oases of activity, leveraging the strength of our stabilizer muscles to propel us towards our goals.
Read also:
- Harness The Power Of Movement: Elevate Your Health With Walking, Running, and FluidStance
- Balancing Act: A Mom’s Journey On The Farm And At Work With FluidStance
- Balance Board Vs. Wobble Board: Which Is Better For Your Workspace?
Frequently Asked Questions About Stabilizer Muscles
What are stabilizer muscles?
Stabilizer muscles are a group of muscles that stabilize one part of the body, allowing other parts to move freely. They're the unsung heroes working quietly in the background, ensuring our movements are smooth and coordinated. These muscles support the skeletal structure, including joints, helping prevent injury and maintain posture.
Why are stabilizer muscles important?
Stabilizer muscles are crucial for maintaining balance, proper posture, and overall movement efficiency. Strengthening these muscles can reduce the risk of injuries, improve athletic performance, and enhance daily activities by making them more manageable and less tiring. For professionals who spend a lot of time at desks, emphasizing stabilizer muscle health can mitigate common aches and pains associated with sedentary lifestyles.
How do stabilizer muscles differ from prime movers?
While stabilizer muscles focus on providing stability and support, prime movers are the muscles primarily responsible for executing specific movements. For example, in a bicep curl, the bicep is the prime mover performing the curling action, while the stabilizer muscles in the shoulder and elbow joints work to maintain proper alignment and posture throughout the movement.
What are examples of stabilizer muscles?
Some key stabilizer muscles include the transversus abdominis and multifidus in the core, the rotator cuff muscles in the shoulder, the gluteus medius in the hips, and the quadratus lumborum in the lower back. Each plays a vital role in supporting its respective joints and contributing to overall stability.
How can I train my stabilizer muscles?
Training stabilizer muscles often involves exercises that promote balance and stability. Activities like yoga and pilates that focus on core strength and balance can also help.
Are stabilizer muscles used in everyday activities?
Absolutely! Stabilizer muscles are engaged in almost every movement we make, from walking and climbing stairs to reaching for items and standing at a desk. Strengthening these muscles may help you enjoy improved efficiency and ease in performing daily activities, leading to a more active and fulfilling lifestyle.
What role do stabilizer muscles play in injury prevention?
Stabilizer muscles play a significant role in injury prevention by providing stability to the joints and supporting the body through various movements. Strong stabilizer muscles can prevent undue stress on joints and ligaments, reducing the risk of acute and overuse injuries.
What exercises improve stabilizer muscle strength?
Exercises that focus on balance and body control help improve stabilizer muscle strength. This includes using balance boards, practicing yoga or Pilates, performing exercises on unstable surfaces like Bosu balls, and incorporating single-leg exercises or movements that engage the core and require body alignment.

Leave a comment